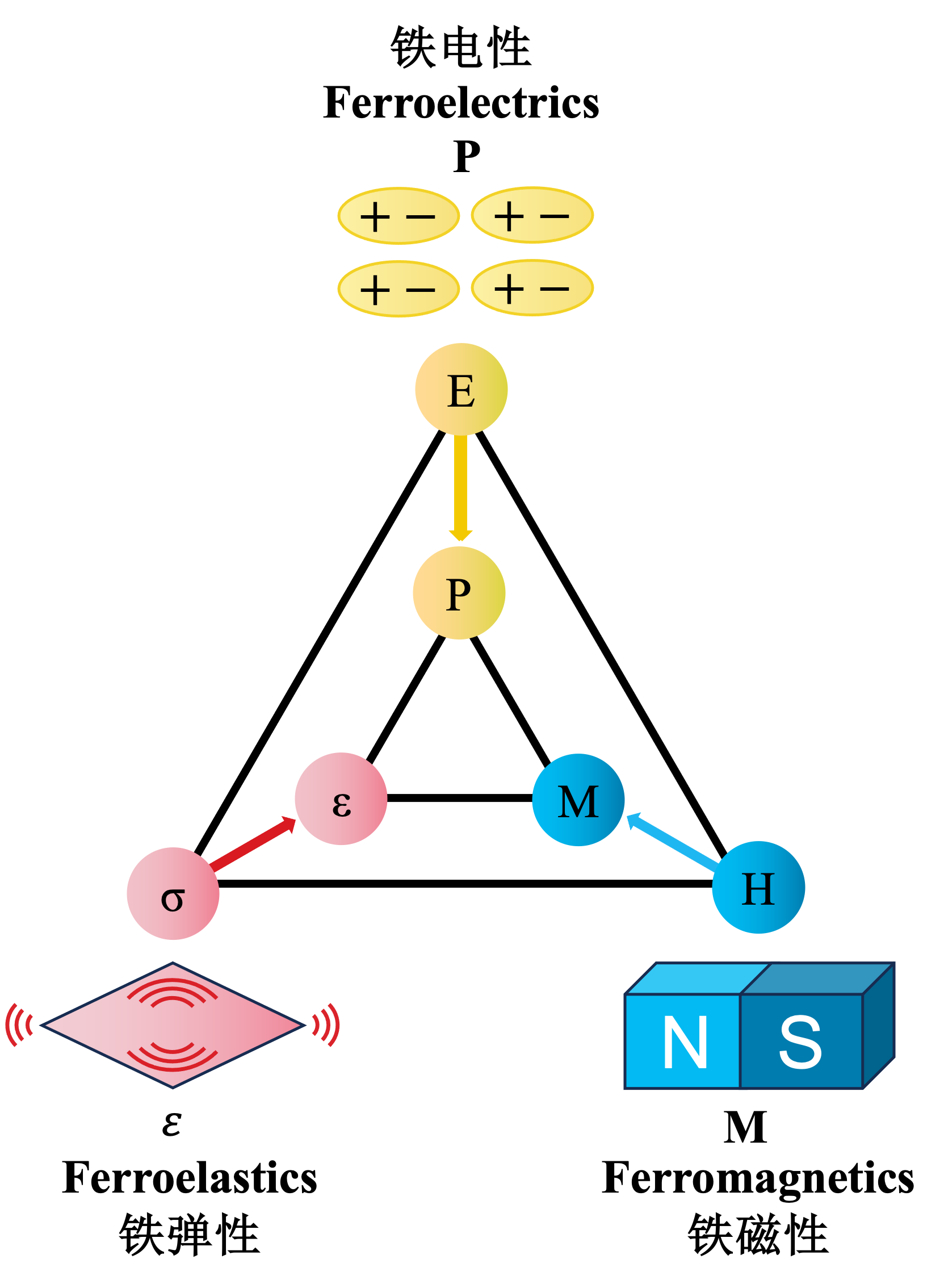
铁性:
自发的电极化、磁极化或应变,且可以通过相应外场,如电场、磁场或应力进行调控的特性。主要包括铁电性、铁磁性、铁弹性。铁性材料在信息存储与处理、储能等领域有着诸多应用和潜在应用。
Ferroic Properties:
A class of materials that exhibit spontaneous polarization, magnetization, or strain, which can be manipulated through external stimuli such as electric fields, magnetic fields, or mechanical stress. Ferroic materials mainly include ferroelectricity, ferromagnetism, and ferroelasticity. Ferroics have numerous applications and potential applications in information storage and processing, energy storage, etc.
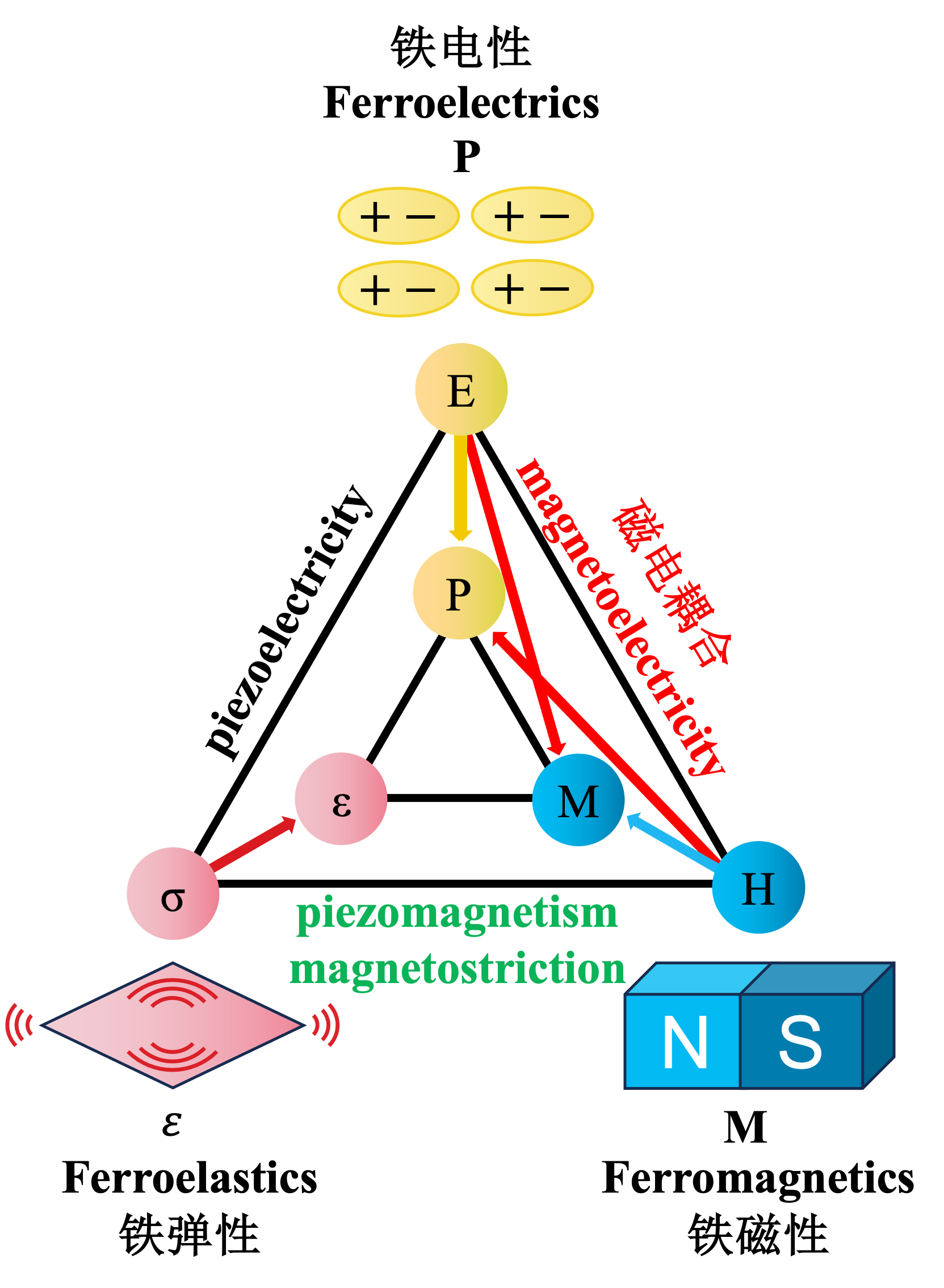
多铁性与磁电耦合效应:
多铁性材料是指同时具有多种铁性的材料,一般来说特指同时具有铁磁性和铁电性的材料。
磁电耦合效应指的是在某些材料中,磁性和电性之间相互关联的现象。当施加外部电场时,可以引起材料的磁性变化;而当施加外部磁场时,材料的电性也会发生变化。
通常多铁材料具有一定的磁电耦合效应,在存储器、传感器和自旋电子学等领域有重要应用前景。
Multiferroics and Magnetoelectric Coupling Effect:
Multiferroic materials refer to those that possess multiple ferroic properties, specifically those that exhibit both ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity simultaneously. Magnetoelectric coupling effect refers to the phenomenon where magnetic and electric properties are interrelated. That is, when an external electric field is applied, it can induce changes in the material’s magnetic properties; conversely, applying an external magnetic field can alter the material’s electrical properties. Typically, multiferroic materials exhibit certain magnetoelectric coupling effect, which holds significant potential for applications in memory storage, sensors, and spintronics.

钙钛矿氧化物:
钙钛矿氧化物是一类具有特定晶体结构的材料,其化学通式为 ABO3,其中 A 和 B 是不同的阳离子。钙钛矿结构以钙钛矿(CaTiO3)为原型,因其独特的结构而得名。不少钙钛矿氧化物是铁性甚至是多铁性材料,例如BiFeO3、La1-xSrxMnO3等等。
Perovskite oxides:
Perovskite oxides are a class of materials that possess a specific crystal structure, typically with the chemical formula ABO3, where A and B are different cations. The perovskite structure is named after the mineral calcium titanate (CaTiO3), which serves as its prototype due to its unique structure. Many perovskite oxides exhibit ferroic or multiferroic properties, such as BiFeO3 and La1-xSrxMnO3.

脉冲激光沉积:
脉冲激光沉积是一种先进的薄膜制备技术,通过使用高能脉冲激光照射靶材,使其表面瞬间蒸发或升华,形成等离子体,并将材料沉积在基底上。该方法具有高灵活性,能够在各种基底上沉积金属、氧化物、氮化物等多种材料,适用于铁性材料、超导等领域的应用。由于其优异的界面质量和纳米级厚度控制,脉冲激光沉积在材料科学和纳米技术中发挥着重要作用。
Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) :
PLD is an advanced thin film fabrication technique that uses high-energy pulsed lasers to irradiate a target material, causing its surface to instantaneously evaporate or sublimate and form plasma, which deposits the material onto a substrate. This method offers high versatility, allowing the deposition of various materials, including metals, oxides, and nitrides, on different substrates, making it suitable for applications in fields such as ferroic materials and superconductors. Due to its excellent interface quality and nanometer-scale thickness control, PLD plays a significant role in materials science and nanotechnology.
